示例代码:
- GitHub:GitHub - Max-Qiu/demo-SpringBoot2: SpringBoot2.x整合各种第三方组件的示例代码
- Gitee:demo-SpringBoot2: SpringBoot2.x整合各种第三方组件的示例代码
本文档整理自视频教程:尚硅谷_SpringMVC视频教程,并对其扩充
环境介绍:本文直接使用 Maven 环境以及 SpringBoot 2.6.x ,不同于视频教程中的先建立web项目再拷贝jar包
建立SpringBoot项目添加如下核心依赖即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
基本介绍
Spring MVC使用@RequestMapping注解为控制器指定可以处理哪些URL请求@RequestMapping注解在控制器的类定义及方法定义处都可标注
匹配规则
- 修饰Controller类:
提供初步的请求映射信息。相对于 WEB 应用的根目录 - 修饰Controller类内的方法:
提供进一步的细分映射信息。相对于类定义处的URL。
若类定义处未标注@RequestMapping,则方法处标记的URL相对于 WEB 应用的根目录
即最终访问的URL大致为: http://[IP]:[端口]/[类上的URL]/[方法上的URL]
特殊的,若 @RequestMapping() 填写含有 / 的字符串,例如: / 、 abc/ 、 /abc 或 /abc/ 等,具体下文示例说明
PS:示例中的 @ResponseBody 定义返回体,此处不做详细介绍
示例1:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("")
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("")
@ResponseBody
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}
请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080 ,若请求 http://127.0.0.1:8080/ 会自动去掉最后的 /
- 示例中类上的
@RequestMapping可以省去,也可以写成@RequestMapping("/"),且访问时URL会自动去掉/ - 示例中方法上的
@RequestMapping也可以写成@RequestMapping("/"),且访问时URL会自动去掉/
示例2:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("")
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("abc")
@ResponseBody
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}
请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc 或 http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/ 均可以访问,但URL不会自动去掉最后一个 /
- 若类的修改为
/,方法的不变,对请求地址均不会产生影响 - 若类的不变,方法修改为
"/abc",对请求地址均不会产生影响 - 若类的不变,方法修改为
"/abc/",则只有http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/能够访问
示例3:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("abc")
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("")
@ResponseBody
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}
请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc 或 http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/ 均可以访问,但URL不会自动去掉最后一个 /
- 示例中若类的修改为
"abc/"或"/abc/",方法的不变,则只有http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/能够访问 - 同示例2:方法修改为
"/",类的不变,也只有http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/能够访问
示例4:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("abc")
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("def")
@ResponseBody
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}
请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/def 或 http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/def/ 均可以访问,但URL不会自动去掉最后一个 /
- 中若方法的不变,类的修改为
"/abc"、"abc/"、"/abc/"对请求地址均不会产生影响 - 若方法的修改为
"/def"对请求地址也不会产生影响 - 同示例2:方法修改为
"def/"或"/def/",则只有http://127.0.0.1:8080/abc/def/可以访问
示例5:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("a/b")
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("c/d")
@ResponseBody
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}
请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080/a/b/c/d 或 http://127.0.0.1:8080/a/b/c/d/ 均可以访问,但URL不会自动去掉最后一个 /
- 若中方法的不变,类的修改为
"/a/b"、"a/b/"、"/a/b/"对请求地址均不会产生影响 - 若方法的修改为
"/c/d"对请求地址也不会产生影响 - 同示例2:方法修改为
"c/d/"或"/c/d/",则只有http://127.0.0.1:8080/a/b/c/d/可以访问
关于 / 的总结
- 根路径若为空,则端口号后面的
/会自动去除 - 定义前的
/若不写,则会自动补全 - 方法定义最后的
/若不写,则UML结尾有无/均可以访问 - 方法定义最后的
/若写了,则UML结尾必须加/才能访问 - 若定义的URL中间有
/则访问也要加/ - 若类定义的结尾有
/且方法定义的开头有/,重复的/会自动。
请求方式
用于区分请求方式,在 @RequestMapping 中使用 method = RequestMethod.??? 配置,一般配合restful风格的URL一起使用,具体协议种类如下:
| 方式 | 简写 |
|---|---|
| GET | @GetMapping |
| POST | @PostMapping |
| PUT | @PutMapping |
| DELETE | @DeleteMapping |
| PATCH | @PatchMapping |
| OPTIONS | |
| HEAD | |
| TRACE |
示例1
@Controller
@RequestMapping("request")
public class RequestController {
/**
* get
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "get", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String get() {
return "get";
}
/**
* GetMapping
*/
@GetMapping(value = "get2")
@ResponseBody
public String get2() {
return "get2";
}
/**
* post
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "post", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String post() {
return "post";
}
/**
* PostMapping
*/
@PostMapping("post2")
@ResponseBody
public String post2() {
return "post2";
}
}
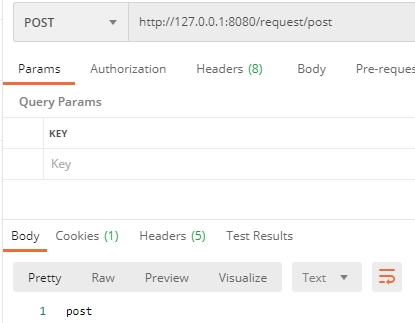
- 访问
http://127.0.0.1:8080/request/get可正常返回 - 访问
http://127.0.0.1:8080/request/post需要使用POST方式,可以借助Postman工具,如下图
请求参数和请求头
在 @RequestMapping 可以添加 params 和 headers 进行更加精确的映射请求
params和headers支持简单达式,如下:
param1:请求必包含名为param1请求参数!param1:请求不包含名为param1请求参数param1 != value1:请求包含名为param1请求参数但其值不为value1{"param1=value1", "param2"}:请求必包含名为param1和param2两个请求参数且param1参数值必为value1
示例
@Controller
@RequestMapping("request")
public class RequestController {
/**
* 使用 params 更加精确的映射请求
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "params", params = {"username", "age!=10"})
@ResponseBody
public String params() {
return "params";
}
/**
* 使用 headers 更加精确的映射请求
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "headers", headers = {"Accept-Language=zh-CN,zh;q=0.9"})
@ResponseBody
public String headers() {
return "headers";
}
}
- params:
- 必须携带
username才可以正常访问,例如:http://127.0.0.1:8080/request/params?username=1 - 当携带
age=10参数时无法访问,例如:http://127.0.0.1:8080/request/params?username=1&age=10
- 必须携带
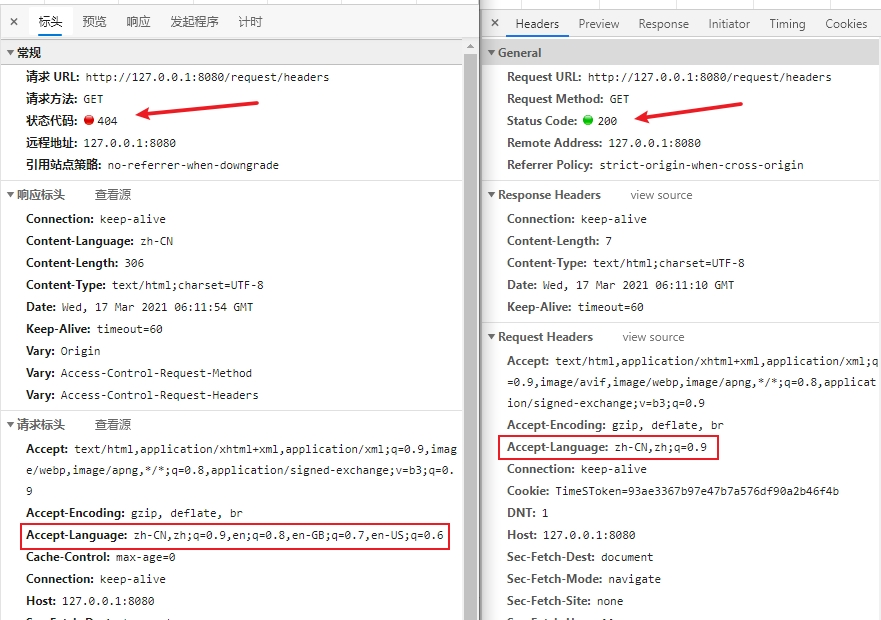
- headers:如下图,使用不同的浏览器访问
http://127.0.0.1:8080/request/headers,当请求头完全匹配才能正常访问
Ant 风格资源地址
Ant 风格资源地址支持三种匹配符:
- ?:匹配文件名中的一个字符
- *:匹配文件名中的任意字符
- **:匹配多层路径
示例
@Controller
@RequestMapping("request")
public class RequestController {
/**
* ?:匹配一个字符(若多个字符需要多个?)
*/
@RequestMapping("/ant/ab?")
@ResponseBody
public String antPath1() {
return "/ant/ab?";
}
/**
* *:匹配任意字符(字符中间不能有 / )
*/
@RequestMapping("/ant/*/abc")
@ResponseBody
public String antPath2() {
return "/ant/*/abc";
}
/**
* **:匹配多层路径(字符中间可以有 / 也可以没有 / )
*/
@RequestMapping("/ant/**/abc")
@ResponseBody
public String antPath3() {
return "/ant/**/abc";
}
}
/ant/ab?http://127.0.0.1:8080/request/ant/abahttp://127.0.0.1:8080/request/ant/abb- ……
/ant/*/abchttp://127.0.0.1:8080/request/ant/a/abchttp://127.0.0.1:8080/request/ant/ab/abc- ……
/ant/**/abchttp://127.0.0.1:8080/request/ant/a/c/abchttp://127.0.0.1:8080/request/ant/ab/c/abchttp://127.0.0.1:8080/request/ant/a/abc(若没有单个*的匹配规则,则也可以匹配到)- ……
原文:SpringMVC:接收数据 - @PathVariable、@RequestParam、@RequestBody、@RequestHeader、@CookieValue