1.Ehcache介绍
Ehcache是一个用Java实现的简单、高速、线程安全的缓存管理类库。具体快速、简单、低消耗、依赖性小、扩展性强、支持对象或序列化缓存、支持缓存或元素的失效、提供LRU/LFU/FIFO缓存策略、支持内存缓存及磁盘缓存、采用分布式缓存机制等特点.
2.引入依赖
在项目的pom.xml中添加下面这三个依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
-
cache-api是JSR-107 Cache的规范,定义了一列接口规范(但是这只是一种规范,需要使用它的实现,例如ehcache3.x、Hazelcast等)。 -
ehcache是ehcache的功能包。 - springBoot要支持第三方缓存的话,还需要引入
spring-boot-starter-cache。
3.配置属性
3.1 配置application.properties
在application.properties添加如下配置:
# 可选,配置了spring.cache.jcache.config属性会自动装配JCacheCacheManager
spring.cache.type=jcache
# 指定ehcache的配置文件所在的位置
spring.cache.jcache.config=classpath:ehcache-3.x.xml
3.2配置ehcache-3.x.xml
在resources文件夹下新建ehcache-3.x.xml,添加如下内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<eh:config
xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance'
xmlns:eh='http://www.ehcache.org/v3'
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.ehcache.org/v3 http://www.ehcache.org/schema/ehcache-core-3.3.xsd">
<!--指定缓存目录-->
<eh:persistence directory="${java.io.tmpdir}/cache-data"/>
<!--缓存模板-->
<eh:cache-template name="default">
<eh:expiry>
<eh:ttl unit="seconds">600</eh:ttl>
</eh:expiry>
<eh:resources>
<!--堆内内存可以放2000个条目,超出部分堆外100MB-->
<eh:heap unit="entries">2000</eh:heap>
<eh:offheap unit="MB">100</eh:offheap>
</eh:resources>
</eh:cache-template>
<!--实际的缓存区间,继承了default缓存模板,sample完全使用模板默认-->
<eh:cache alias="sample" uses-template="default"></eh:cache>
<!--下面两个继承了default缓存模板,但覆盖了缓存的过期时间-->
<eh:cache alias="authority_service" uses-template="default">
<eh:expiry>
<eh:ttl unit="hours">1</eh:ttl>
</eh:expiry>
</eh:cache>
<eh:cache alias="shop_service" uses-template="default">
<eh:expiry>
<eh:ttl unit="hours">24</eh:ttl>
</eh:expiry>
</eh:cache>
</eh:config>
更多配置知识,请参考ehcache官网:ehcache XML配置
4.使用示例
4.1 准备一个controller
该controller只有一个方法,获得某类商品的列表:
@RestController
@Validated
@RequestMapping("/v1.0/api/shop")
public class ShopController {
@Autowired
ShopService shopService;
@RequestMapping(value = {"/commodity"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<String> listCommodity (@RequestParam String type) {
System.out.println("ShopController: type is " + type);
return shopService.listCommodity(type);
}
}
4.2 准备一个service
- 在需要使用缓存的Bean上面添加@EnableCaching注解,那该bean具有缓存功能。
- 在需要使用缓存的方法上添加@Cacheable注解,那该方法具有缓存功能(前提是该bean具有缓存的功能)。
注意 : 1和2配合起来才能使某个bean的某个方法具有缓存的功能。
package com.example.demo.service;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@EnableCaching
public class ShopService {
// value:使用叫做'shop_service'的缓存器
// key: 缓存的key等于#type,即传入的key值
// condition:缓存的条件,当#type等于phone时,才进行缓存
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "shop_service", key = "#type", condition = "#type == 'phone'")
public List<String> listCommodity(String type) {
System.out.println("ShopService: 调用了listCommodity");
List<String> commodities = new ArrayList<>();
if (type.equals("phone")) {
commodities.add("Apple");
commodities.add("HuaWei");
} else {
commodities.add("others");
}
return commodities;
}
}
4.3 启动springBoot,进行测试
使用浏览器,发送4个请求:
- http://localhost:8080/v1.0/api/shop/commodity?type=phone
- http://localhost:8080/v1.0/api/shop/commodity?type=phone
- http://localhost:8080/v1.0/api/shop/commodity?type=computer
- http://localhost:8080/v1.0/api/shop/commodity?type=computer
后台打印的日志如下:
ShopController: type is phone
ShopService: 调用了listCommodity
ShopController: type is phone
ShopController: type is computer
ShopService: 调用了listCommodity
ShopController: type is computer
ShopService: 调用了listCommodity
4.4 结果分析
第一次发送请求,符合缓存的条件,由于没有缓存,于是执行了service的逻辑,并将结果缓存到了ehcache中。
第二次发送请求,符合缓存的条件,由于已经缓存了结果,直接从ehcache中拿取缓存的结果返回,没有进入到service的逻辑。
第三次和第四次都不符合缓存的条件,需要进入到service的逻辑计算结果。
5.Ehcache使用场景
使用的过程中,根据优点和缺点进行权衡后再应用到项目中去,Ehcache缓存也是如此,在实际工作有很多使用场景,通常将Ehcache作为Redis的二次缓存使用。
5.1 Ehcache的适用场景
(1) 比较少的更新数据表的情况下
Ehcache作为Hibernate的缓存时,在进行修改表数据(save、update、delete等)的时候,Ehcache会自动把缓存中关于此表的所有缓存全部删除掉,这样做只是能达到同步,但对于数据经常修改的表来说,可能就失去了缓存的意义了。
(2)对一致性要求不高的情况下
因为Ehcache本地缓存的特性,目前无法很好的解决不同服务器缓存同步的问题,所以在一致性要求高的场合下,建议使用Redis、Memcached等集中式缓存。
5.2Ehcache的缺陷
(1) 缓存漂移
每个应用节点只管理自己的缓存,在更新某个节点的时候,不会影响到其他的节点,这样数据之间可能就不同步了。
(2) 数据库瓶颈
对于单实例的应用来说,缓存可以保护数据库的读风暴;但是在集群的环境下,每一个应用节点都要定期保存数据更新,节点越多,要维持这样的情况对数据库的开销也越大。
5.3 Ehcache的正确打开方式
我们在项目中使用集中式缓存(Redis或Memcached等)通常都是检查缓存中是否存在期望的数据,如果存在直接将数据返回,如果不存在就查询数据库然后再将数据缓存,而后将结果返回。这时候如果缓存系统因为某些原因宕机,造成服务无法访问,那么大量的请求将直接穿透到数据库,对数据库造成巨大的压力。
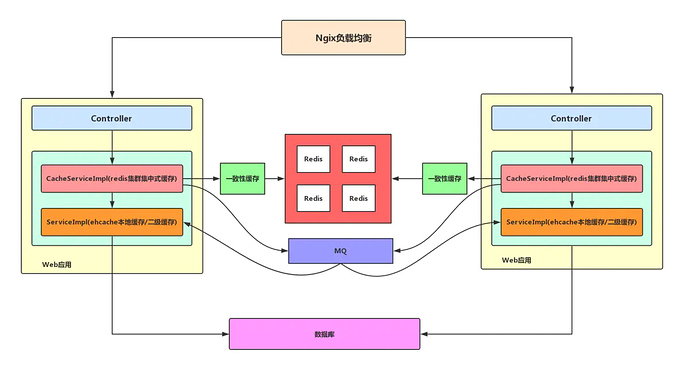
针对上述情况,我们有多种可行的解决方法,其中一种方案是将Ehcache作为集中式缓存的二级本地缓存,这样当缓存系统宕机后,服务器应用的本地缓存还能继续抗住大量请求。
使用了Ehcache作为本地缓存后,可能会出现本地缓存与缓存系统之间出现数据不一致的情况,因为本地缓存是在服务器应用中存在,在实际生产环境中必定是多台服务器分别部署,如何能够在更新缓存系统数据的同时,也能够更新Ehcache的缓存数据,以及保证不同服务器间Ehcache本地缓存数据的同步问题。
一般有两种解决方案可供参考:
第一种:定时轮询
每台应用服务器定时轮询Redis缓存,更新本地的Ehcache缓存。
第二种:主动通知
每台应用服务器的Ehcache同步侦听MQ消息,通过MQ推送的方式,将redis中更新的缓存数据推送到每台应用服务器中。
针对上述的分析,可形成如下的缓存方案: